本篇文章内容转自:阮一峰博客博文
关于Centos7安装和rpm安装可以参考:传送门
Elastic 的底层是开源库 Lucene。但是,你没法直接用 Lucene,必须自己写代码去调用它的接口。Elastic 是 Lucene 的封装,提供了 REST API 的操作接口,开箱即用。
本文从零开始,讲解如何使用 Elastic 搭建自己的全文搜索引擎。每一步都有详细的说明,大家跟着做就能学会。
一、安装
Elastic 需要 Java 8 环境。如果你的机器还没安装 Java,上百度。注意要保证环境变量JAVA_HOME正确设置。
安装完 Java,就可以跟着官方文档安装 Elastic。直接下载压缩包比较简单。我自己的环境是Java 10
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.5.1.zip
unzip elasticsearch-5.5.1.zip
cd elasticsearch-5.5.1/ 接着,进入解压后的目录,运行下面的命令,启动 Elastic。
./bin/elasticsearch
如果这时报错”max virtual memory areas vm.maxmapcount [65530] is too low”,要运行下面的命令。
sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
如果一切正常,Elastic 就会在默认的9200端口运行。这时,打开另一个命令行窗口,请求该端口,会得到说明信息。
curl localhost:9200
{
"name" : "atntrTf",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "tf9250XhQ6ee4h7YI11anA",
"version" : {
"number" : "5.5.1",
"build_hash" : "19c13d0",
"build_date" : "2017-07-18T20:44:24.823Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "6.6.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}上面代码中,请求9200端口,Elastic 返回一个 JSON 对象,包含当前节点、集群、版本等信息。
按下 Ctrl + C,Elastic 就会停止运行。
默认情况下,Elastic 只允许本机访问,如果需要远程访问,可以修改 Elastic 安装目录的config/elasticsearch.yml文件,去掉network.host的注释,将它的值改成0.0.0.0,然后重新启动 Elastic
network.host: 0.0.0.0
上面代码中,设成0.0.0.0让任何人都可以访问。线上服务不要这样设置,要设成具体的 IP。
二、基本概念
2.1 Node 与 Cluster
Elastic 本质上是一个分布式数据库,允许多台服务器协同工作,每台服务器可以运行多个 Elastic 实例。
单个 Elastic 实例称为一个节点(node)。一组节点构成一个集群(cluster)。
2.2 Index
Elastic 会索引所有字段,经过处理后写入一个反向索引(Inverted Index)。查找数据的时候,直接查找该索引。
所以,Elastic 数据管理的顶层单位就叫做 Index(索引)。它是单个数据库的同义词。每个 Index (即数据库)的名字必须是小写。
下面的命令可以查看当前节点的所有 Index。
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v'
2.3 Document
Index 里面单条的记录称为 Document(文档)。许多条 Document 构成了一个 Index。
Document 使用 JSON 格式表示,下面是一个例子。
{
"user": "张三",
"title": "工程师",
"desc": "数据库管理"
}同一个 Index 里面的 Document,不要求有相同的结构(scheme),但是最好保持相同,这样有利于提高搜索效率。
2.4 Type
Document 可以分组,比如weather这个 Index 里面,可以按城市分组(北京和上海),也可以按气候分组(晴天和雨天)。这种分组就叫做 Type,它是虚拟的逻辑分组,用来过滤 Document。
不同的 Type 应该有相似的结构(schema),举例来说,id字段不能在这个组是字符串,在另一个组是数值。这是与关系型数据库的表的一个区别。性质完全不同的数据(比如products和logs)应该存成两个 Index,而不是一个 Index 里面的两个 Type(虽然可以做到)。
下面的命令可以列出每个 Index 所包含的 Type。
curl 'localhost:9200/_mapping?pretty=true'
根据规划,Elastic 6.x 版只允许每个 Index 包含一个 Type,7.x 版将会彻底移除 Type。
三、新建和删除 Index
新建 Index,可以直接向 Elastic 服务器发出 PUT 请求。下面的例子是新建一个名叫weather的 Index。
curl -X PUT 'localhost:9200/weather'
服务器返回一个 JSON 对象,里面的acknowledged字段表示操作成功。
{
"acknowledged":true,
"shards_acknowledged":true
}然后,我们发出 DELETE 请求,删除这个 Index。
curl -X DELETE 'localhost:9200/weather'
四、中文分词设置
首先,安装中文分词插件。这里使用的是 ik,也可以考虑其他插件(比如 smartcn)。
./bin/elasticsearch-plugin install https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases/download/v5.5.1/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-5.5.1.zip
上面代码安装的是5.5.1版的插件,与 Elastic 5.5.1 配合使用。
接着,重新启动 Elastic,就会自动加载这个新安装的插件。
然后,新建一个 Index,指定需要分词的字段。这一步根据数据结构而异,下面的命令只针对本文。基本上,凡是需要搜索的中文字段,都要单独设置一下
curl -X PUT 'localhost:9200/accounts' -d '
{
"mappings": {
"person": {
"properties": {
"user": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"desc": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
}'上面代码中,首先新建一个名称为accounts的 Index,里面有一个名称为person的 Type。person有三个字段。
user
title
desc这三个字段都是中文,而且类型都是文本(text),所以需要指定中文分词器,不能使用默认的英文分词器。
Elastic 的分词器称为 analyzer。我们对每个字段指定分词器。
"user": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}上面代码中,analyzer是字段文本的分词器,search_analyzer是搜索词的分词器。ik_max_word分词器是插件ik提供的,可以对文本进行最大数量的分词。
五、数据操作
5.1 新增记录
向指定的 /Index/Type 发送 PUT 请求,就可以在 Index 里面新增一条记录。比如,向/accounts/person发送请求,就可以新增一条人员记录。
curl -X PUT 'localhost:9200/accounts/person/1' -d '
{
"user": "张三",
"title": "工程师",
"desc": "数据库管理"
}' 服务器返回的 JSON 对象,会给出 Index、Type、Id、Version 等信息。
{
"_index":"accounts",
"_type":"person",
"_id":"1",
"_version":1,
"result":"created",
"_shards":{"total":2,"successful":1,"failed":0},
"created":true
}如果你仔细看,会发现请求路径是/accounts/person/1,最后的1是该条记录的 Id。它不一定是数字,任意字符串(比如abc)都可以。
新增记录的时候,也可以不指定 Id,这时要改成 POST 请求。
curl -X POST 'localhost:9200/accounts/person' -d '
{
"user": "李四",
"title": "工程师",
"desc": "系统管理"
}'上面代码中,向/accounts/person发出一个 POST 请求,添加一个记录。这时,服务器返回的 JSON 对象里面,_id字段就是一个随机字符串。
{
"_index":"accounts",
"_type":"person",
"_id":"AV3qGfrC6jMbsbXb6k1p",
"_version":1,
"result":"created",
"_shards":{"total":2,"successful":1,"failed":0},
"created":true
}注意,如果没有先创建 Index(这个例子是accounts),直接执行上面的命令,Elastic 也不会报错,而是直接生成指定的 Index。所以,打字的时候要小心,不要写错 Index 的名称。
5.2 查看记录
向/Index/Type/Id发出 GET 请求,就可以查看这条记录。
curl 'localhost:9200/accounts/person/1?pretty=true'
上面代码请求查看/accounts/person/1这条记录,URL 的参数pretty=true表示以易读的格式返回。
返回的数据中,found字段表示查询成功,_source字段返回原始记录。
{
"_index" : "accounts",
"_type" : "person",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"user" : "张三",
"title" : "工程师",
"desc" : "数据库管理"
}
}如果 Id 不正确,就查不到数据,found字段就是false。
curl 'localhost:9200/weather/beijing/abc?pretty=true'
{
"_index" : "accounts",
"_type" : "person",
"_id" : "abc",
"found" : false
}5.3 删除记录
删除记录就是发出 DELETE 请求。
curl -X DELETE 'localhost:9200/accounts/person/1'这里先不要删除这条记录,后面还要用到。
5.4 更新记录
更新记录就是使用 PUT 请求,重新发送一次数据
$ curl -X PUT 'localhost:9200/accounts/person/1' -d '
{
"user" : "张三",
"title" : "工程师",
"desc" : "数据库管理,软件开发"
}'
{
"_index":"accounts",
"_type":"person",
"_id":"1",
"_version":2,
"result":"updated",
"_shards":{"total":2,"successful":1,"failed":0},
"created":false
}上面代码中,我们将原始数据从”数据库管理”改成”数据库管理,软件开发”。 返回结果里面,有几个字段发生了变化。
"_version" : 2,
"result" : "updated",
"created" : false可以看到,记录的 Id 没变,但是版本(version)从1变成2,操作类型(result)从created变成updated,created字段变成false,因为这次不是新建记录。
六、数据查询
6.1 返回所有记录
使用 GET 方法,直接请求/Index/Type/_search,就会返回所有记录。
$ curl 'localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search'
{
"took":2,
"timed_out":false,
"_shards":{"total":5,"successful":5,"failed":0},
"hits":{
"total":2,
"max_score":1.0,
"hits":[
{
"_index":"accounts",
"_type":"person",
"_id":"AV3qGfrC6jMbsbXb6k1p",
"_score":1.0,
"_source": {
"user": "李四",
"title": "工程师",
"desc": "系统管理"
}
},
{
"_index":"accounts",
"_type":"person",
"_id":"1",
"_score":1.0,
"_source": {
"user" : "张三",
"title" : "工程师",
"desc" : "数据库管理,软件开发"
}
}
]
}
}上面代码中,返回结果的 took字段表示该操作的耗时(单位为毫秒),timed_out字段表示是否超时,hits字段表示命中的记录,里面子字段的含义如下。
total:返回记录数,本例是2条。
max_score:最高的匹配程度,本例是1.0。
hits:返回的记录组成的数组。返回的记录中,每条记录都有一个_score字段,表示匹配的程序,默认是按照这个字段降序排列。
6.2 全文搜索
Elastic 的查询非常特别,使用自己的查询语法,要求 GET 请求带有数据体。
curl 'localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search' -d '
{
"query" : { "match" : { "desc" : "软件" }}
}'上面代码使用 Match 查询,指定的匹配条件是desc字段里面包含”软件”这个词。返回结果如下。
{
"took":3,
"timed_out":false,
"_shards":{"total":5,"successful":5,"failed":0},
"hits":{
"total":1,
"max_score":0.28582606,
"hits":[
{
"_index":"accounts",
"_type":"person",
"_id":"1",
"_score":0.28582606,
"_source": {
"user" : "张三",
"title" : "工程师",
"desc" : "数据库管理,软件开发"
}
}
]
}
}Elastic 默认一次返回10条结果,可以通过size字段改变这个设置。
curl 'localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search' -d '
{
"query" : { "match" : { "desc" : "管理" }},
"size": 1
}'上面代码指定,每次只返回一条结果。
还可以通过from字段,指定位移。
curl 'localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search' -d '
{
"query" : { "match" : { "desc" : "管理" }},
"from": 1,
"size": 1
}'上面代码指定,从位置1开始(默认是从位置0开始),只返回一条结果。
6.3 逻辑运算
如果有多个搜索关键字, Elastic 认为它们是or关系。
$ curl 'localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search' -d '
{
"query" : { "match" : { "desc" : "软件 系统" }}
}'上面代码搜索的是软件 or 系统。
如果要执行多个关键词的and搜索,必须使用布尔查询。
curl 'localhost:9200/accounts/person/_search' -d '
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "desc": "软件" } },
{ "match": { "desc": "系统" } }
]
}
}
}'补充
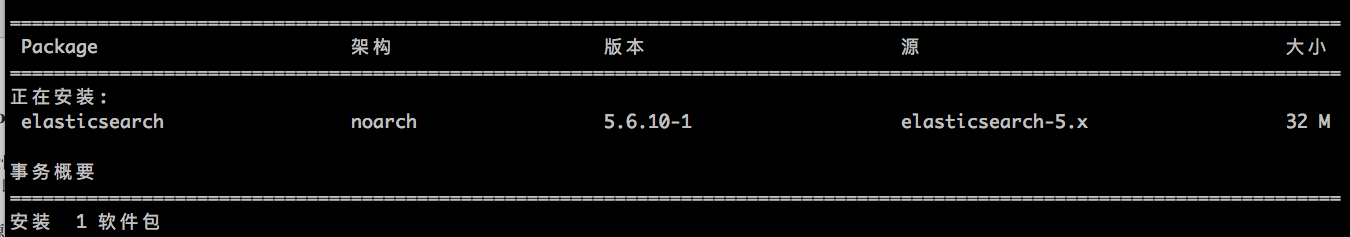
centos7安装elasticsearch
在一般情况下、尤其是生产环境、希望elasticsearch开机自启动、如果在centos7写入systemclt.service比较难写资料也较少。用yum源安装则是最好的选择方式,当然elasticsearch本来就是开箱即用的软件。
注意:如果出现下载失败可能域名没有解析到
wget报错信息
wget: unable to resolve host address ‘artifacts.elastic.co’
vim /etc/resolv.conf
添加两行内容为下
nameserver 8.8.8.8 #google域名服务器
nameserver 8.8.4.4 #google域名服务器
yum源
[elasticsearch-5.x]
name=Elasticsearch repository for 5.x packages
baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/5.x/yum
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
enabled=1
autorefresh=1
type=rpm-md默认安装则是最新版
yum install elasticsearch
Centos7中的systemctl.service脚本内容
[Unit]
Description=Elasticsearch
Documentation=http://www.elastic.co
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
[Service]
Environment=ES_HOME=/usr/share/elasticsearch
Environment=CONF_DIR=/etc/elasticsearch
Environment=DATA_DIR=/var/lib/elasticsearch
Environment=LOG_DIR=/var/log/elasticsearch
Environment=PID_DIR=/var/run/elasticsearch
EnvironmentFile=-/etc/sysconfig/elasticsearch
WorkingDirectory=/usr/share/elasticsearch
User=elasticsearch
Group=elasticsearch
ExecStartPre=/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-systemd-pre-exec
ExecStart=/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch \
-p ${PID_DIR}/elasticsearch.pid \
--quiet \
-Edefault.path.logs=${LOG_DIR} \
-Edefault.path.data=${DATA_DIR} \
-Edefault.path.conf=${CONF_DIR}
# StandardOutput is configured to redirect to journalctl since
# some error messages may be logged in standard output before
# elasticsearch logging system is initialized. Elasticsearch
# stores its logs in /var/log/elasticsearch and does not use
# journalctl by default. If you also want to enable journalctl
# logging, you can simply remove the "quiet" option from ExecStart.
StandardOutput=journal
StandardError=inherit
# Specifies the maximum file descriptor number that can be opened by this process
LimitNOFILE=65536
# Specifies the maximum number of processes
LimitNPROC=2048
# Specifies the maximum size of virtual memory
LimitAS=infinity
# Specifies the maximum file size
LimitFSIZE=infinity
# Disable timeout logic and wait until process is stopped
TimeoutStopSec=0
# SIGTERM signal is used to stop the Java process
KillSignal=SIGTERM
# Send the signal only to the JVM rather than its control group
KillMode=process
# Java process is never killed
SendSIGKILL=no
# When a JVM receives a SIGTERM signal it exits with code 143
SuccessExitStatus=143
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
# Built for distribution-5.6.10 (distribution)rpm安装
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.6.10.rpm
rpm --install elasticsearch-5.6.10.rpm
在centos6中的脚本、摘选别的的(没有测试)
在/etc/init.d目录下新建文件elasticsearch
#!/bin/sh
#chkconfig: 2345 80 05
#description: elasticsearch
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_112
export JAVA_BIN=/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_112/bin
export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin
export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar
export JAVA_HOME JAVA_BIN PATH CLASSPATH
case "$1" in
start)
su lyt<<!
cd /home/lyt/dev-repo/elk5/elasticsearch-5.6.9
./bin/elasticsearch -d
!
echo "elasticsearch startup"
;;
stop)
es_pid=`ps aux|grep elasticsearch | grep -v 'grep elasticsearch' | awk '{print $2}'`
kill -9 $es_pid
echo "elasticsearch stopped"
;;
restart)
es_pid=`ps aux|grep elasticsearch | grep -v 'grep elasticsearch' | awk '{print $2}'`
kill -9 $es_pid
echo "elasticsearch stopped"
su lyt<<!
cd /home/lyt/dev-repo/elk5/elasticsearch-5.6.9
./bin/elasticsearch -d
!
echo "elasticsearch startup"
;;
*)
echo "start|stop|restart"
;;
esac
exit $?保存退出,赋予执行权限
chmod +x elasticsearch
添加到开机启动任务
chkconfig -add elasticsearch
如果不设置开机启动的话,也可以使用service elasticsearch start/stop/restart来操作
安装的注意事项
官方推荐安装JDK8
由于我自己安装的Jdk版本10,不是yum安装的 :/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin 没有可执行文件、所以启动elasticsearch不成功。
执行下面命令创建软连接。
[root@iZm5e0ssd5luniclrse6wfZ /usr/java/jdk-10.0.1/bin]
# ln -s /usr/java/jdk-10.0.1/bin/java /usr/bin/java
[root@iZm5e0ssd5luniclrse6wfZ /usr/java/jdk-10.0.1/bin]
# ln -s /usr/java/jdk-10.0.1/bin/javac /usr/bin/javac
[root@iZm5e0ssd5luniclrse6wfZ /usr/java/jdk-10.0.1/bin]
# ln -s /usr/java/jdk-10.0.1/bin/jar /usr/bin/jarsystemctl start elasticsearch.service
安装Ik分词器
ik分词器github地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases
选择下载5.6.10的zip下载既用
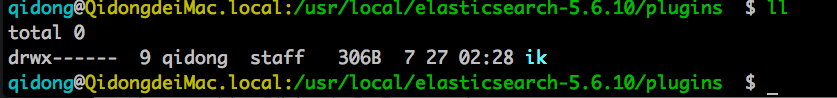
更改文件夹名称为ik
cd /usr/local/elasticsearch-5.6.10
mv ./ik /usr/local/elasticsearch-5.6.10/plugins
vim ik/config/stopword.dic
a
an
and
are
as
at
be
but
by
for
if
in
into
is
it
no
not
of
on
or
such
that
the
their
then
there
these
they
this
to
was
will
with
是
的
也
了
仍
从
以
使
则
却
又
及
对
就
井
很
或
把
着
给
而
被
让
在
还
比
等
当
与
于
但测试
qidong@QidongdeiMac.local:/Users/qidong $ curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/_analyze?pretty=true&analyzer=ik_max_word' -d 查看的分词是
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "查看",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "分词",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
}
]
}ik_max_word 和 ik_smart 什么区别?
ik_max_word: 会将文本做最细粒度的拆分,比如会将“中华人民共和国国歌”拆分为“中华人民共和国,中华人民,中华,华人,人民共和国,人民,人,民,共和国,共和,和,国国,国歌”,会穷尽各种可能的组合;
ik_smart: 会做最粗粒度的拆分,比如会将“中华人民共和国国歌”拆分为“中华人民共和国,国歌”。
